ChatArea Component
The ChatArea component is the central part of the chat application, responsible for displaying messages and providing the interface for sending messages.
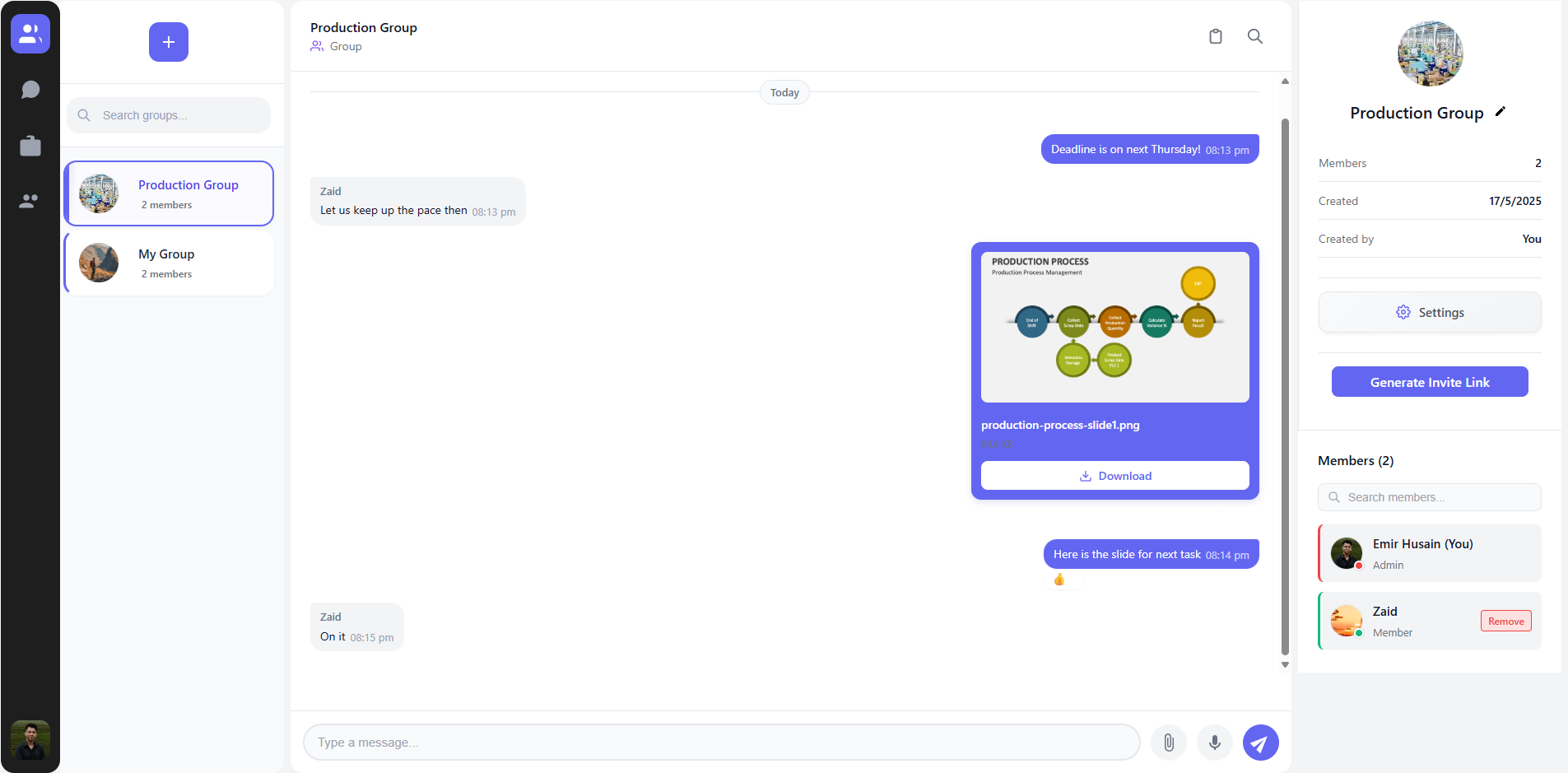
Overview
The ChatArea component is a complex component that handles:
- Displaying messages in a scrollable container
- Sending text messages
- Uploading and sending files
- Recording and sending voice messages
- Message reactions
- Message editing and deletion
- Showing typing indicators
- User blocking UI elements
- Notifications for new messages
Component Structure
The ChatArea component is structured as follows:
// File: src/components/chat/ChatArea.jsx
import { useState, useRef, useEffect } from 'react';
import { useAuth } from '../../contexts/AuthContext';
import { useChat } from '../../contexts/ChatContext';
import styles from './ChatArea.module.css';
import React from 'react';
import ChatAreaSkeleton from './ChatAreaSkeleton';
import MessageReactions from './MessageReactions';
import MessageSearch from './MessageSearch';
import VoiceRecorder from './VoiceRecorder';
import AudioPlayer from './AudioPlayer';
import LogViewer from './LogViewer';
import { ref, get } from 'firebase/database';
import { db } from '../../config/firebase';
export default function ChatArea() {
// Component state and logic
// ...
return (
<div className={styles.chatArea}>
{/* Header */}
<div className={styles.header}>
{/* ... */}
</div>
{/* Blocked banner (if applicable) */}
{isOtherUserBlocked && (
<div className={styles.blockedBanner}>
{/* ... */}
</div>
)}
{/* Message list */}
<div className={styles.messageList} ref={messageListRef}>
{/* Messages */}
{/* ... */}
</div>
{/* Scroll button */}
{renderScrollButton()}
{/* Typing indicators */}
<div className={styles.typingIndicatorContainer}>
{renderTypingIndicators()}
</div>
{/* Message form */}
<form onSubmit={handleSend} className={styles.messageForm}>
{/* ... */}
</form>
{/* Additional panels */}
{showSearchPanel && <MessageSearch /* ... */ />}
{showLogViewer && <LogViewer /* ... */ />}
</div>
);
}
Props & Context
The ChatArea component doesn't receive any props directly but uses several context providers:
ChatContext
The component consumes the following from ChatContext:
const {
currentChat,
messages,
sendMessage,
sendFileMessage,
sendVoiceMessage,
fileUploads,
handleVote,
markChatAsRead,
FILE_SIZE_LIMIT,
ALLOWED_FILE_TYPES,
typingUsers,
setTypingStatus,
loadMoreMessages,
hasMoreMessages,
loading,
editMessage,
deleteMessage,
setMessages,
isCurrentUserAdmin,
isUserBlocked
} = useChat();
AuthContext
The component uses the authenticated user from AuthContext:
const { user } = useAuth();
Key State Variables
The component manages several pieces of internal state:
// Message input
const [newMessage, setNewMessage] = useState('');
const [fileUploadError, setFileUploadError] = useState('');
// UI states
const [showVoiceRecorder, setShowVoiceRecorder] = useState(false);
const [showScrollButton, setShowScrollButton] = useState(false);
const [buttonFading, setButtonFading] = useState(false);
const [newMessageReceived, setNewMessageReceived] = useState(false);
// Message loading states
const [isLoadingMore, setIsLoadingMore] = useState(false);
const [reachedTop, setReachedTop] = useState(false);
const [messagesLoading, setMessagesLoading] = useState(false);
const [isAtTop, setIsAtTop] = useState(false);
// Message editing states
const [editingMessage, setEditingMessage] = useState(null);
const [editingContent, setEditingContent] = useState('');
const [editError, setEditError] = useState('');
const [deleteConfirm, setDeleteConfirm] = useState(null);
// Reply functionality
const [replyingTo, setReplyingTo] = useState(null);
// User blocking
const [otherUserId, setOtherUserId] = useState(null);
const [isOtherUserBlocked, setIsOtherUserBlocked] = useState(false);
Key Functions
Message Sending
The component has several functions for sending different types of messages:
Text Messages
const handleSend = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
if (!newMessage.trim() || !currentChat?.id) return;
// Check if user is blocked
// ...
// Create optimistic message
// ...
// Send the message
sendMessage(message, replyingTo?.id || null);
// Clear the input
setNewMessage('');
// Clear typing status
setTypingStatus(false);
};
File Messages
const handleFileUpload = async (e) => {
const file = e.target.files[0];
if (!file) return;
// Validate file type and size
// ...
// Process and send the file
await sendFileMessage(processedFile, progressCallback, replyingTo?.id || null);
};
Voice Messages
const handleSendVoice = async (audioBlob, duration) => {
// Check if user is blocked
// ...
// Send the voice message
await sendVoiceMessage(audioBlob, duration, replyingTo?.id || null);
};
Scrolling and Message Loading
The component includes functions for managing the message list scrolling:
// Load more messages when user scrolls to top
const handleLoadMore = () => {
if (isLoadingMore || !loadMoreMessages || !isAtTop) return;
setIsLoadingMore(true);
loadMoreMessages(20).then((hasMore) => {
// Update UI based on whether more messages exist
// ...
});
};
// Scroll to bottom of messages
const scrollToBottom = (smooth = true) => {
if (!messageListRef.current) return;
messageListRef.current.scrollTo({
top: messageListRef.current.scrollHeight,
behavior: smooth ? 'smooth' : 'auto'
});
};
Message Editing
Functions for editing and deleting messages:
const handleStartEdit = (message) => {
// Validate edit permissions
// ...
setEditingMessage(message);
setEditingContent(message.content);
};
const handleSaveEdit = async () => {
if (!editingMessage || !editingContent.trim()) return;
await editMessage(editingMessage.id, editingContent.trim());
setEditingMessage(null);
};
const handleDeleteMessage = async () => {
if (!deleteConfirm) return;
await deleteMessage(deleteConfirm.id);
setDeleteConfirm(null);
};
User Blocking Integration
The component checks if the current user has blocked the other participant:
useEffect(() => {
if (!otherUserId || !isUserBlocked) {
setIsOtherUserBlocked(false);
return;
}
const blocked = isUserBlocked(otherUserId);
setIsOtherUserBlocked(blocked);
}, [otherUserId, isUserBlocked]);
If a user is blocked, the UI changes:
- A blocked banner is displayed
- The message input is disabled
- A different placeholder text is shown
Rendering Messages
Messages are rendered based on their type:
// Text messages
{!message.type && !message.deleted && (
<div className={styles.bubble}>
{message.content}
{/* ... */}
</div>
)}
// File messages
{message.type === 'file' && (
<div className={styles.fileMessage}>
{renderFilePreview(message)}
{/* ... */}
</div>
)}
// Voice messages
{message.type === 'voice' && (
<div className={styles.voiceMessage}>
{renderVoiceMessage(message)}
{/* ... */}
</div>
)}
CSS Modules
The component uses CSS Modules for styling:
import styles from './ChatArea.module.css';
This approach ensures style encapsulation, preventing conflicts with other components.
Error Handling
The component includes various error handling mechanisms:
try {
// Component logic
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error:', error);
setFileUploadError(error.message || 'An error occurred');
// Clear error after delay
setTimeout(() => setFileUploadError(''), 5000);
}
Performance Considerations
The component implements several performance optimizations:
- Message Pagination: Loading messages in batches
- Memoization: Preventing unnecessary re-renders
- Debouncing: Limiting typing indicator updates
- Optimistic UI: Showing message before server confirmation
- Image Compression: Reducing file sizes before upload
Usage Example
The ChatArea component is typically used in a layout like this:
function ChatPage() {
return (
<div className="chat-container">
<ChatSidebar />
<div className="main-content">
<ChatArea />
</div>
<DirectMessagePanel />
</div>
);
}
Related Components
The ChatArea component works closely with:
MessageReactions: Handles emoji reactions to messagesVoiceRecorder: Provides voice recording UI and functionalityAudioPlayer: Renders playable voice messagesChatAreaSkeleton: Displays a loading placeholder
Best Practices
When modifying the ChatArea component:
- Maintain the state structure to avoid breaking scroll behavior
- Use the provided hooks and context methods
- Add new message types by extending the rendering logic
- Test extensively with different message types
- Consider mobile responsiveness for all UI elements