Architecture Overview
This page provides a high-level overview of the React Firebase Chat Application's architecture, explaining how the different components work together.
System Architecture
The chat application follows a client-server architecture with Firebase handling the backend functionality:
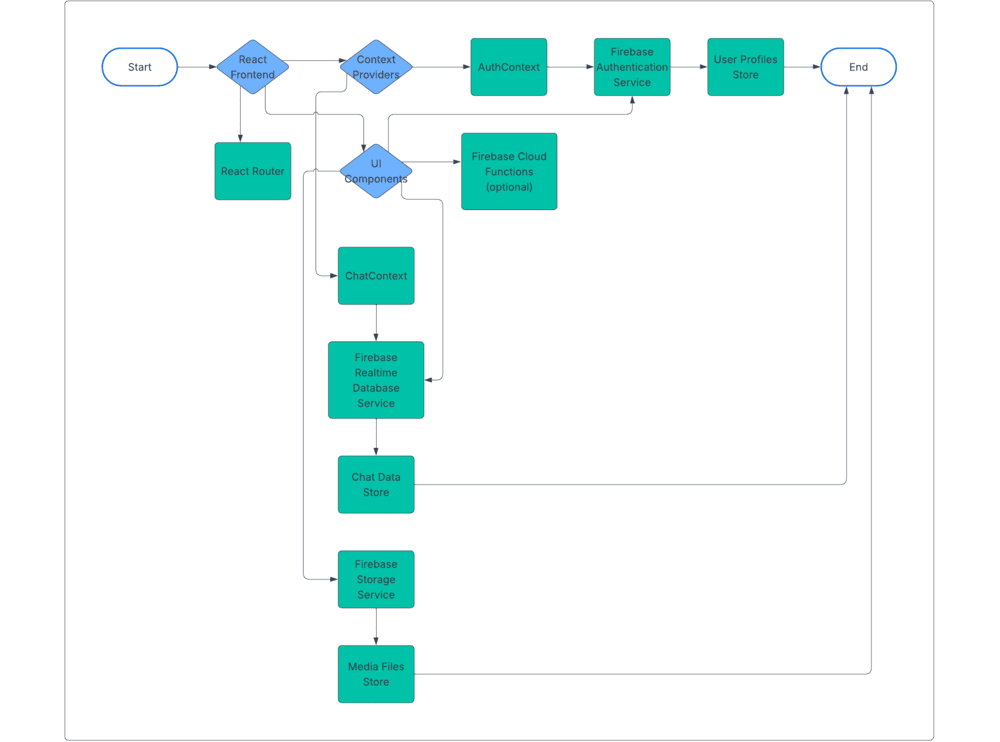
Client-Side (React)
The frontend is built with React, using a modern functional component approach with hooks and context providers for state management.
Server-Side (Firebase)
Firebase provides the backend services:
- Firebase Realtime Database: Stores chat messages, user presence, and typing indicators
- Firestore: Stores user profiles and chat metadata
- Firebase Authentication: Handles user authentication
- Firebase Storage: Stores uploaded files and voice messages
- Firebase Cloud Functions (optional): For advanced serverless functionality
Core Components
The application is structured around several key components:
State Management
The app uses React Context API for state management, with two main contexts:
- AuthContext: Manages user authentication state
- ChatContext: Manages chat-related state (messages, chats, users)
Component Architecture
The main components include:
- App.jsx: Main application component
- ChatSidebar: List of chat conversations and user profile
- ChatArea: Message display and input
- DirectMessagePanel: User details and actions for direct messages
- GroupInfoPanel: Group details and management for group chats
- MessageReactions: Emoji reactions for messages
- VoiceRecorder: Voice message recording functionality
Data Flow
The data flow in the application follows this pattern:
- User Interaction: User performs an action (sends a message, uploads a file)
- Context Action: The appropriate context method is called
- Firebase Update: Data is written to Firebase
- Real-time Listeners: Firebase listeners detect the change
- State Update: Context state is updated with the new data
- Component Re-render: Components render with the updated data
Real-time Communication
Real-time communication is handled through Firebase Realtime Database listeners, which:
- Listen for changes to specific database paths
- Update the application state when changes occur
- Automatically handle connection state and reconnection
Authentication Flow
The authentication process follows this flow:
- User enters credentials or uses a social provider
- Firebase Authentication verifies the credentials
- On successful authentication, a user profile is created or retrieved
- AuthContext is updated with the authenticated user
- The application displays the authenticated UI
Permissions Model
The application uses Firebase security rules to enforce permissions:
- Public Data: Available to all authenticated users (e.g., user profiles)
- Private Data: Limited to specific users (e.g., direct messages)
- Group Data: Limited to group members
- Admin Actions: Limited to group admins
Error Handling
Error handling is managed at multiple levels:
- Component Level: UI feedback for form errors
- Context Level: Global error state for authentication and chat errors
- Firebase Level: Security rules prevent unauthorized access
Optimizations
The application includes several performance optimizations:
- Pagination: Messages are loaded in batches
- Memoization: React.memo and useMemo for expensive components
- Lazy Loading: Components and assets are loaded on demand
- Debouncing: Typing indicators are debounced to reduce database writes
Next Steps
To dive deeper into the architecture:
- Explore the data model to understand the database structure
- Learn about the Firebase integration details
- Review the folder structure to understand the code organization